The method of producing the 3-diamensional image of an object due to the interference phenomena of coherent light waves on a photographic plate is known as holography. The idea of holography was first developed by Dennis Gabber in 1948. The invention of laser during 1960 enhanced research in this field.
When an object is photographed by a camera, a 2-dimensional image of 3-dimensional object is obtained. Here only the amplitude of the light wave is recorded on the photographic film. In holography, both the phase and the amplitude of the light waves are recorded in the film. The resulting photograph is called hologram. In Greek, ‘holo’ means whole and ‘graphy’ means writing. So holography stands for whole writing. The recorded hologram has no resemblance to the original object. It has in it a coded form of information of the object. The image is reproduced by a process called reconstruction.
Recording of a hologram
The experimental arrangement for the recording of a hologram using a laser beam is shown below:
When an object is photographed by a camera, a 2-dimensional image of 3-dimensional object is obtained. Here only the amplitude of the light wave is recorded on the photographic film. In holography, both the phase and the amplitude of the light waves are recorded in the film. The resulting photograph is called hologram. In Greek, ‘holo’ means whole and ‘graphy’ means writing. So holography stands for whole writing. The recorded hologram has no resemblance to the original object. It has in it a coded form of information of the object. The image is reproduced by a process called reconstruction.
Recording of a hologram
The experimental arrangement for the recording of a hologram using a laser beam is shown below:
 A laser beam from a source is made to fall on an optical device called beam splitter. A part of the beam splitter is made to fall on a mirror M1. The beam is reflected waves from the mirror and made to fall on the object. The reflected waves from the surface of the object, called object wave, is made to fall on the photographic plate. The other part of the beam is made to fall on a mirror M2 and then to photographic plate. This beam is called reference wave. The object wave and reference wave interfere and the interference pattern characteristic of the object is recorded on the photographic plate. This recorded interference pattern gives hologram.
A laser beam from a source is made to fall on an optical device called beam splitter. A part of the beam splitter is made to fall on a mirror M1. The beam is reflected waves from the mirror and made to fall on the object. The reflected waves from the surface of the object, called object wave, is made to fall on the photographic plate. The other part of the beam is made to fall on a mirror M2 and then to photographic plate. This beam is called reference wave. The object wave and reference wave interfere and the interference pattern characteristic of the object is recorded on the photographic plate. This recorded interference pattern gives hologram.Reconstruction of images
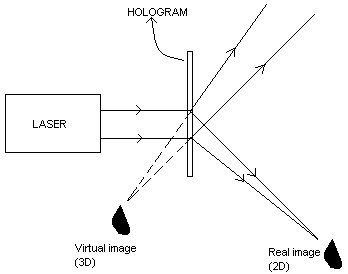
In order to view the image, hologram is to be illuminated with the laser having the same wavelength used for recording of the hologram. Illumination of the hologram results in two images - a two dimensional real image and a three dimensional virtual image.













No comments:
Post a Comment